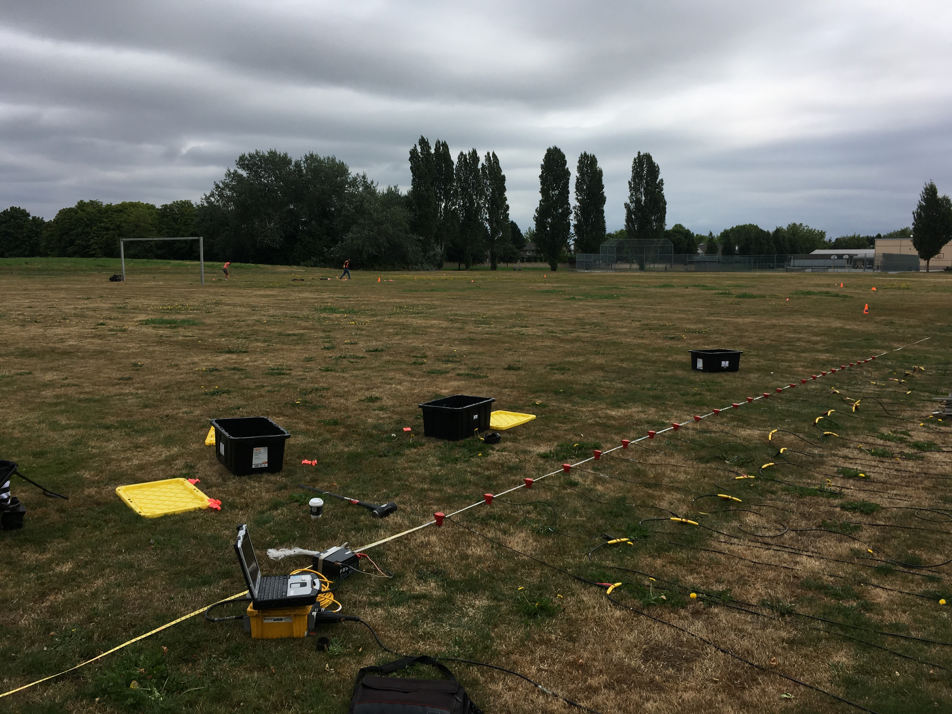
The quality of seismic microzonation mapping depends on the accuracy and amount of geodata “behind” the maps. Non-invasive seismic methods are used primarily to supplement previously collected subsurface information accumulated in the project’s geodatabase. Details about the types of non-invasive seismic methods that are used are described below. A total of four summer field campaigns will be accomplished to provide adequate coverage across the region.
.MASW (Multi-channel Analysis of Surface Waves)
MASW is an active-source seismic method to measure surface wave dispersion across a linear array of geophones. Active-source methods involve generating seismic waves using a seismic source (e.g., hammer impact, weight drop). MASW recordings are obtained in this project using a linear array of 24 vertical-component geophones connected to a Geode seismograph. MASW testing measures the phase velocity of Rayleigh waves along the geophone array. Geophone spacings of 0.5 to 3 m are used. MASW testing provides higher frequency (shorter wavelength) Rayleigh wave dispersion estimates. Both MASW and AVA dispersion estimates are combined into a full dispersion curve which is inverted for the site’s shear wave velocity (Vs) depth profile(s).
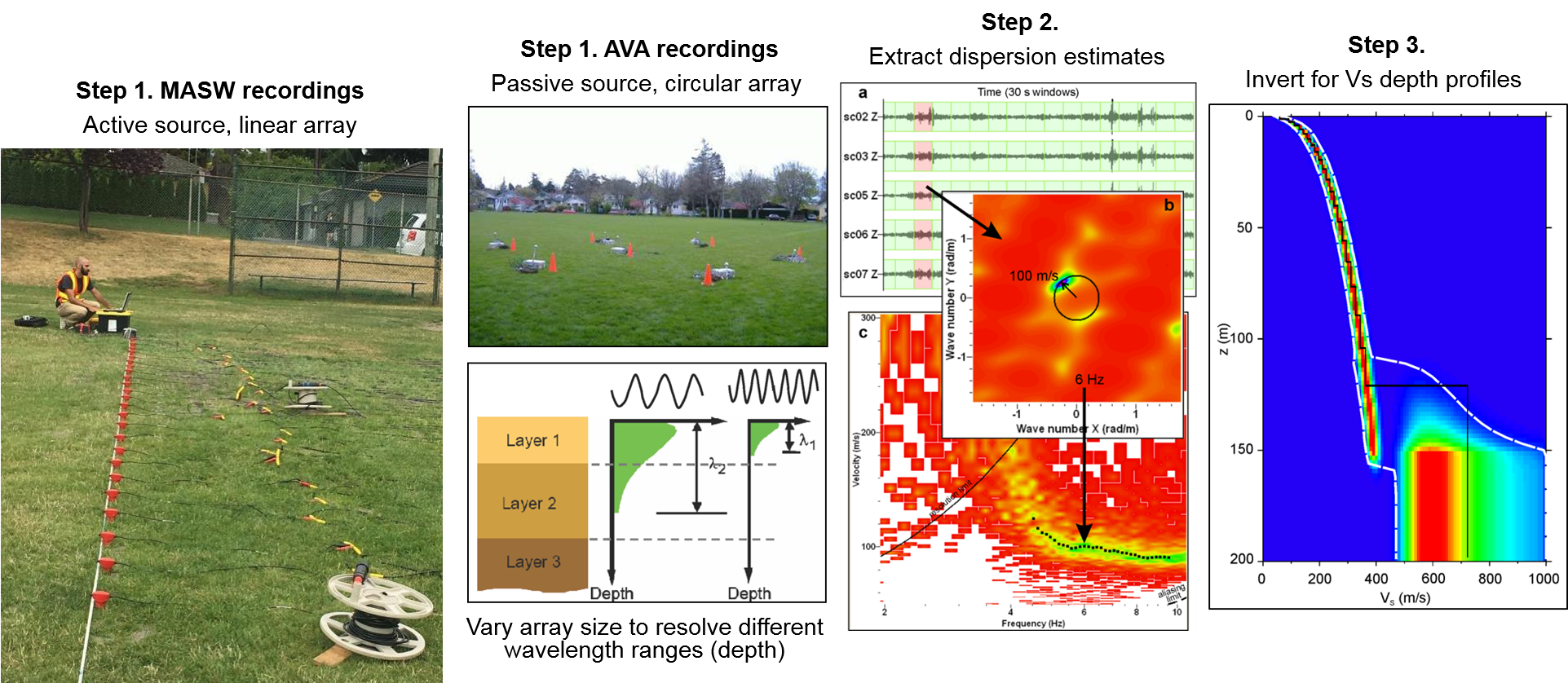
.AVA (Ambient Vibration Array)
AVA is a passive-source seismic method to measure surface wave dispersion across a two-dimensional (2D) array of geophones. Passive-source methods involve recording background seismic noise, called ambient vibrations or microtremors, generated by natural phenomena (e.g., tides, wind) and human activities (e.g., traffic, machinery, pedestrians). Because we do not know the direction of the seismic energy (we don’t generate the seismic waves), we need a 2D array geometry (seismic waves can come from any direction). AVA recordings are obtained in this project using up to 7 three-component Tromino® seismometers placed in a circular array geometry. AVA testing measures the phase velocity of Rayleigh or Love waves across the 2D array (between receiver pairs). Array radius is typically varied from 5 to 30 m. AVA testing provides lower frequency (longer wavelength) Rayleigh wave dispersion estimates. Both AVA and MASW dispersion estimates are combined into a full dispersion curve which is inverted for the site’s shear wave velocity (Vs) depth profile(s).

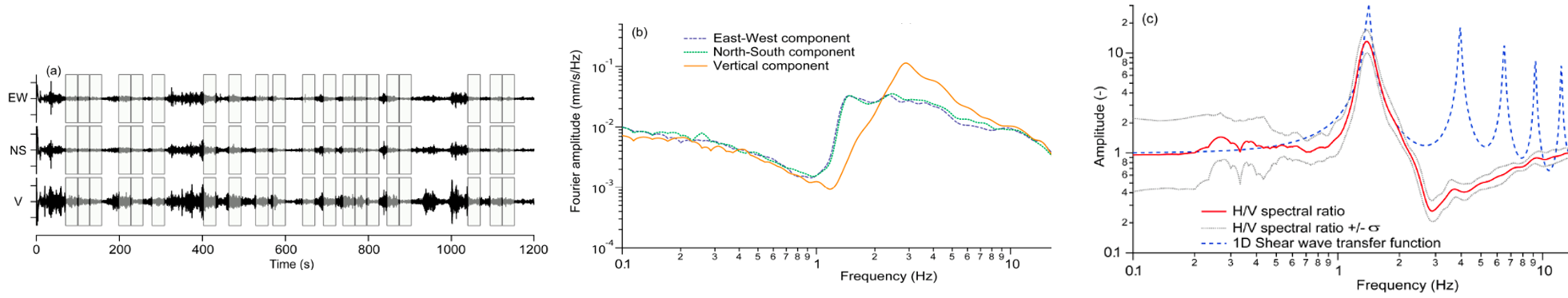
.MHVSR (Microtremor Horizontal-to-Vertical Spectral Ratio)
The MHVSR method is an analysis technique that calculates the ratio of the horizontal-to-vertical Fourier spectra derived from microtremor recordings, typically recorded at a specific location by a three-component seismometer. In general, MHVSR analysis is currently applied for retrieval and evaluation of the resonance frequencies of unconsolidated sediments over high-velocity bedrock. Maximum amplification occurs at the peak frequency or fundamental resonance frequency which is related to the soil’s thickness and average stiffness.